|
JOIN THE BEST
MCITP Boot Camp,
MCSE
Boot Camp also CCNA ,
CCNP Certification
Boot Camp Training program.
100% Guaranteed
- Lowest Fees, Highest
Passing Rate.
MCSE Boot Camp Certification
MCITP MCSE and CCNA Certification Notes Series :
MCSE 2016 Boot Camp
:
Azure Boot camp :
CCNA / CCNAX
Boot Camp:
CCNA Boot Camp
Cisco Hierarchical Model:
For more information about this, please read our
separate tutorial titled "The
Cisco Hierarchical Model".
OSI Model:
The OSI model is a layered model and a
conceptual standard used for defining standards
to promote multi-vendor integration as well as
maintain constant interfaces and isolate changes
of implementation to a single layer. It is NOT
application or protocol specific. In order to
pass any Cisco exam, you need to know the OSI
model inside and out.
The OSI Model consists of 7 layers as follows:
|
Layer |
Description |
Device |
Protocol |
|
Application |
Provides network access for
applications, flow control and error
recovery. Provides communications
services to applications by identifying
and establishing the availability of
other computers as well as to determine
if sufficient resources exist for
communication purposes. |
Gateway |
NCP, SMB, SMTP, FTP, SNMP, Telnet,
Appletalk |
|
Presentation |
Performs protocol conversion, encryption
and data compression |
Gateway and redirectors |
NCP, AFP, TDI |
|
Session |
Allows 2 applications to communicate
over a network by opening a session and
synchronizing the involved computers.
Handles connection establishment, data
transfer and connection release |
Gateway |
NetBios |
|
Transport |
Repackages messages into smaller
formats, provides error free delivery
and error handling functions |
Gateway |
NetBEUI, TCP, SPX, and NWLink |
|
Network |
Handles addressing, translates logical
addresses and names to physical
addresses, routing and traffic
management. |
Router and brouter |
IP, IPX, NWLink, NetBEUI |
|
**Data Link |
Packages raw bits into frames making it
transmitable across a network link and
includes a cyclical redundancy check(CRC).
It consists of the LLC sublayer and the
MAC sublayer. The MAC sublayer is
important to remember, as it is
responsible for appending the MAC
address of the next hop to the frame
header. On the contrary, LLC sublayer
uses Destination Service Access Points
and Source Service Access Points to
create links for the MAC sublayers. |
Switch, bridge and brouter |
None |
|
Physical |
Physical layer works with the physical
media for transmitting and receiving
data bits via certain encoding schemes.
It also includes specifications for
certain mechanical connection features,
such as the adaptor connector. |
Multiplexer and repeater |
None |
Here is an easy way to memorize the order of the
layers:
All People Seem To Need Data Processing.
The first letter of each word corresponds to the
first letter of one of the layers. It is a
little corny, but it works.
|
Class |
Range |
Explanation |
|
A |
1-126 |
IP addresses can be class A, B or C.
Class A addresses are for networks with
a large number of hosts. The first octet
is the netid and the 3 remaining octets
are the hostid. Class B addresses are
used in medium to large networks with
the first 2 octets making up the netid
and the remaining 2 are the hostid. A
class C is for smaller networks with the
first 3 octets making up the netid and
the last octet comprising the hostid.
The later two classes arenít used for
networks. |
|
B |
128-191 |
|
C |
192-223 |
|
D |
224-239 (Multicasting) |
|
E |
240-255 (Experimental) |
A subnet mask blocks out a portion of an IP
address and is used to differentiate between the
hostid and netid. The default subnet masks are
as follows:
|
Class |
Default Subnet |
# of Subnets |
# of Hosts Per Subnet |
|
Class A |
255.0.0.0 |
126 |
16,777,214 |
|
Class B |
255.255.0.0 |
16,384 |
65,534 |
|
Class C |
255.255.255.0 |
2,097,152 |
254 |
In these cases, the part of the IP address
blocked out by 255 is the Net ID.
3COMís IP addressing tutorial is
just superior. It covers basic IP addressing
options as well as subnetting and VLSM/CIDR.
IPX/SPX:
IPX will also be an important issue to consider
in network management given the fact there many
companies still use Netware servers. There are
two parts to every IPX Network address - the
Network ID and the Host ID. The first 8 hex
digits represent the network ID, while the
remaining hex digits represent the host ID,
which is most likely the same as the MAC
address, meaning we do not need to manually
assign node addresses. Note that valid
hexadecimal digits range from 0 through 9, and
hexadecimal letters range from A through F.
FFFFFFFF in hexadecimal notation = 4292967295 in
decimal.
Sequenced Packet Exchange(SPX) belongs to the
Transport layer, and is connection-oriented. It
creates virtual circuits between hosts, and that
each host is given a connection ID in the SPX
header for identifying the connection. Service
Advertisement Protocol(SAP) is used by NetWare
servers to advertise network services via
broadcast at an interval of every 60 minutes by
default.
|
Router User Interface
The Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) is the kernel of Cisco's
Routers and most of their switches.
Cisco IOS software is used to :
- Carry network protocols and functions
- Connect high speed traffic between devices
- Add security, control access, and stop unauthorized network access
- Promote Scalability for ease of network growth and redundancy
- Supply network reliability for connecting to network resources
The IOS can be accessed through the console port, from a modem (auxiliary
port), or through the network via telnet. Access to the IOS command line is
called an EXEC session.
Console Port
- Connect using a RJ-45 port on the back of the router.
- Cable is wired straight through but reversed on one side (rolled cable).
Console
(DTE) |
Console Port |
Console Cable |
Rollover Cable |
| Signal |
RJ-45 Pin |
RJ-45 Pin |
| RTS
|
1
|
8
|
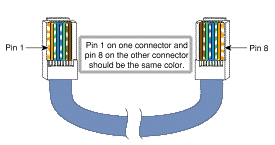 |
| DTR
|
2
|
7
|
| TXD
|
3
|
6
|
| GND
|
4
|
5
|
| GND
|
5
|
4
|
| RXD
|
6
|
3
|
| DSR
|
7
|
2
|
| CTS
|
8
|
1
|
- Cable connects to RJ-45 to DB9 adapter and the PC uses a Terminal Emulation
program set to 9600 baud, 8 bits, N parity, 1 stop bit.
- Console port has no password by default.
Auxiliary Port
- Same as console port and can be used in same way.
- Typically used by having a modem you can use to dial into the router with.
- Useful for configuring a remote router you don't have physical access to.
- If a remote route stops responding, it can still be accessed if it has a
modem on its auxiliary port.
Telnet
- Telephone Network - it emulates a dumb terminal and connects over the
network.
- Can connect from PCs or other routers.
- When logging on to the router, be aware that telnet sends and receives
passwords and usernames in plain text.
Powering up a Cisco Router
- First runs POST (Power On Self Test).
- If POST passes, it loads the IOS from flash memory if present (Flash Memory
is EEPROM).
- IOS will then load the configuration file called startup-configuration,
stored in NVRAM by default.
- If no configuration file is present, the router will bring up setup mode (a
step-by-step process to help you configure a router, it can be run any time by
entering setup at the global configuration command line prompt).
SETUP Mode
Setup mode has two modes, Basic Management and Extended Setup.
Basic Management
- Only gives you enough configurations to allow connectivity to the router.
- Configures only enough connectivity for management of the system.
Extended Setup
- Allows you to configure some global parameters as well as interface
configuration parameters.
- Prompts you to configure each interface on the system.
- Prompts for
- Hostname
- Secret Password
- Enable Password
- VTY Password (used for Telnet Sessions)
- SNMP setup
- Protocols {DECnet, AppleTalk, IP(IP routing -RIP, IGRP, etc)}
- Bridging
- IPX protocol
- Async Lines
- If ISDN BRI interface is present, it prompts for switch type.
- Next configures Interfaces, including IP address and network mask.
- The running-config is shown after the interfaces are configured.
- The last option in setup is a menu of three choices.
- Discard Configuration and go to command line.
- To start setup mode over.
- To save setup to NVRAM to be used at boot up (startup -config).
Command Line Interface
If you choose to skip setup mode, you will be taken to the command line and
the status of all the interfaces will be shown to the screen.
Logging in to the Router
Depending on the port you're using, you might have to press enter to get the
prompt to appear (console port). The first prompt will look like
Routername> the greater than sign at the prompt tells you that you are in
user mode. In user mode you can only view limited statistics of
the router. To change configurations you first need to enter
privileged EXEC mode. This is done by typing enable at
the Routername> prompt, the prompt then changes to Routername#.
This mode supports testing commands, debugging commands, and commands to manage
the router configuration files. To go back to user mode type disable
at the Routername# prompt. If you want to leave completely, type
logout at the user mode prompt. You can also exit from the router
while in privileged mode by typing exit or logout at the
Routername#
prompt.
Global Configuration Mode
Enter this mode from the privileged mode by typing configure terminal
or conf t for short, the prompt will change to Routername(config)#.
Changes made in this mode change the running-config file in DRAM. Use
configure memory to change the startup-config in NVRAM. Using
configure network allows you to change the configuration file on a TFTP
server. If you change the memory or network config files, the router has
to put them into memory (DRAM) in order to work with them, so this will change
your router's current running-config file.
Interfaces
While in global configuration mode you can enter interface configuration mode
and make changes to individual interfaces with the command
Router(config)#interface ethernet 0 or
Router(config)#int e0 for short, this enters into the interface
configuration mode for Ethernet port 0 and changes the prompt to look like
Router(config-if)#.
Subinterfaces
In global configuration mode you can create virtual interfaces, so at the
prompt Routername(config)# type int e0.1 and the prompt will
change to
Routername(config-subif)#. For all practical purposes there isn't a limit
to the amount of subinterfaces an interface can have.
Lines
In global configuration mode you can enter line [aux, vty, console]
to enter commands for the line type. Changes the prompt to
Routername(config-line)#. In line mode you can set passwords, inactivity
timeout times, and number of available lines (vty).
Routing Protocols
In global configuration mode enter router followed by one of the
following protocols:
bgp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
egp Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP)
eigrp Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
igrp Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
isis ISO IS-IS
iso-igrp IGRP for OSI networks
mobile Mobile routes
odr On Demand stub Routes
ospf Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
static Static routes
This will allow you to set parameters for the selected
routing protocol and will change the current prompt to
Routername(config-router)#.
Banners
There are four types of banners: exec, incoming, login, and motd. The banners
are set in global configuration mode with the command:
Router_2(config)#banner motd !
Enter TEXT message. End with the character '!'.
Welcome to Router_2
Only authorized personnel may login
!
Router_2(config)#
A delimiting character is used to set off the message,
in this case the character is the ! symbol.
Adding a Description to an Interface
An interface description is limited to 80 characters and typically describes
the function of the interface.
Router_2(config)#int serial 1
Router_2(config-if)#description Link to East Office
Router_2(config-if)#
|
Call Now : 800-519-
2267
|
Testimonials
|
If you're serious about getting certified,
this is the place to go. Definitely worth
their competitive price. Excellent
instructors, making it possible for anyone
to learn no matter what your level of
experience or knowledge.
Michael Doty
|
 |
Vibrant
offers
MCITP MCSE
certification
training
boot camp
for $5400
all inclusive,
instructor
led at
California
and
Baltimore.
Ref1
:
Ref2
:
link
:
resources
:
Tcp/ip
MCITP MCSE CCNA CCNP Boot Camp Schedule by Vibrant
boot camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp Proven
MCITP MCSE Boot camp Training
for MCITP MCSE Certification Fast
MCITP
MCSE CCNA CCNP Boot Camp Schedule by
Vibrant boot camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp - Proven Boot camp
for MCITP MCSE at Baltimore, Maryland
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp Payment Gateway to get
MCITP MCSE
Certification Fast!
CCNA 801 Boot Camp by Vibrant boot camps,
join MCITP MCSE camps
CCNA Boot Camp by Vibrant boot camps,
join MCITP MCSE camps
CCNP Boot Camp by Vibrant boot camps,
join CCNP camps
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp compare Vibrant boot
camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
Comptia Security+ Boot Camp by
Vibrant boot camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp contact Vibrant boot camps,
join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp course fees Vibrant boot
camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp FAQ by Vibrant boot camps,
join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp location by Vibrant boot
camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp location by Vibrant boot
camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp MCITP MCSE Certification also
MCITP MCSE Training Boot Camp
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp by Vibrant boot
camps, join MCITP MCSE camps, MCITP MCSE Cert
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp by Vibrant boot
camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp by Vibrant boot
camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp by Vibrant boot
camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Security Boot Camp MCITP MCSE
14days all_incl MCITP MCSE Certifiation boot camp
MCITP MCSE Security Boot Camp by
Vibrant boot camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Security Boot Camp by
Vibrant boot camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Security Boot Camp by
Vibrant boot camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Security Boot Camp by
Vibrant boot camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp Payment Gateway to get
MCITP MCSE
Certification Fast!
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp Refunds
MCITP
MCSE CCNA CCNP Boot Camp Register by
Vibrant boot camps
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp Testimonials by Vibrant
boot camps
MCITP MCSE Boot Camp Payment Gateway to get
MCITP MCSE
Certification Fast!
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp MCITP MCSE Certification
also MCITP MCSE Training Boot Camp
Microsoft Vista
Certification Boot Camp for Vista training boot camps
MCITP MCSE CCNA CCNP Boot Camp Register by Vibrant
boot camps
MCITP
MCSE Boot Camp all inclusive bootcamp
Vibrant boot camps, join MCITP MCSE camps
MCITP
MCSE CCNA CCNP Boot Camp Register by
Vibrant boot camps
|
![]() MCITP Boot camp
UK
MCITP Boot camp
UK
![]() MCITP Camp
Thailand
MCITP Camp
Thailand
![]() MCITP
RHCE Boot Camp India
MCITP
RHCE Boot Camp India